
Introduction: Although the IPSS-R stratifies patients with MDS in five risk groups and includes an intermediate-risk group, treatment options are commonly based on the division of the patients into low-risk MDS (LR-MDS) and high-risk MDS (HR-MDS). However, it is not well-defined which cut-off better classifies patients in LR-MDS vs. HR-MDS and, specifically, to which category belongs the intermediate IPSS-R group. A prior study from the International Working Group for the Prognosis of MDS suggested that a cut-off of ≤3.5 points was adequate to identify LR-MDS patients. The aim of the study was to establish the point of the IPSS-R that best divides patients in LR-MDS and HR-MDS and describe the clinical characteristics and outcomes of the intermediate-risk subgroup.
Methods: All patients diagnosed with MDS according to the WHO 2008 from the Spanish Registry of Myelodysplastic Syndromes between 1980 and 2019 were included. Patients with an OS ≥30 months were defined as LR-MDS. The prognostic risk of the patients was performed according to the IPSS-R. The IPSS-R point that dichotomized the patients was obtained in agreement with the value that maximized the log-rank test in the overall survival (OS) analysis and the Youden index. Kaplan-Meier test was used for survival analysis, Cox model to obtain the hazard ratios (HR) and competing risk analysis for the evolution to acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Statistical analysis was performed by software R.
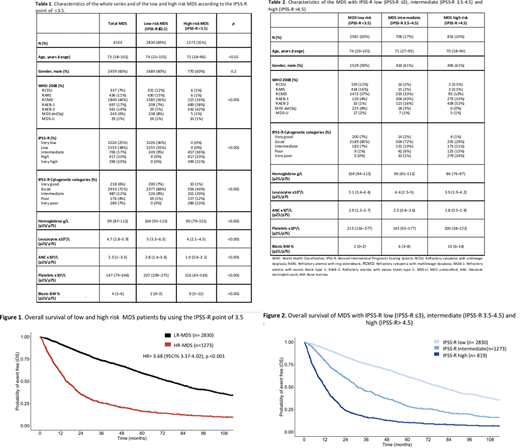
Results: Among 8,107 MDS included in the registry, 4,103 had all the variables to be classified according to the IPSS-R (patients characteristics detailed in table 1). The median follow-up for survivors was 52.7 months (CI95% 49.9-56.5). Median OS was 52.9 months (CI95% 50.2-56). The IPSS-R cut-off that best identified LR-MDS patients was ≤3.5 (75% accuracy to predict OS ≥30 months). According to this value, 2,830 (69%) and 1,273 (31%) patients were classified as LR-MDS and HR-MDS, with a median OS of 75 months (CI95% 71.1-80.7) and 15.4 months (CI95% 14.5-17.4), respectively; [HR= 3.68 (95%CI 3.37-4.02); p<0.001] [Figure 1]. The 3-years cumulative incidence of AML evolution was 5.4% (IC95% 4.5-5.4) in the LR-MDS and 26.8% (IC95% 24.2-29.5) in the HR-MDS [HR= 6.1 (IC95% 4.9-7.5); p<0.001].
When the whole cohort was stratified into MDS with IPSS-R low (IPSS-R ≤3), intermediate (IPSS-R 3.5-4.5), and high (IPSS-R >4.5), median OS was 79, 30.8 and 12.1 months, respectively (Figure 2). Patients characteristics are detailed in table 2. Considering the point of 3.5, most of the intermediate IPSS-R patients (457 of 706, 65%) were upgraded to MDS-HR. Moreover, MDS with intermediate IPSS-R exhibited an OS and a 3 years cumulative incidence of AML evolution [20.7% (CI95% 17.7-24.3)] analogous to MDS with high IPSS-R.
Conclusions: Our study supports the use of a cut-off of ≤3.5 to stratify MDS patients in low and high-risk subgroups, with significant differences in both OS and risk of AML transformation. Intermediate-risk IPSS-R group disclose a clinical outcome resembling more HR-MDS than LR-MDS. Thus, by using this cut-off most of the intermediate IPSS-R MDS patients are indeed considered as higher risk. These findings have relevant clinical implications, as they imply that intermediate-risk patients should be managed as high-risk MDS.
Villacampa:Merck Sharp & Dohme: Honoraria; AstraZeneca: Other: advisory role. Tormo:Celgene: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Pfizer: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Janssen: Honoraria; MSD: Honoraria; Daiichi Sankyo: Honoraria; Servier: Honoraria; Roche: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Astellas: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Ramos:Roche: Other: travel grant; Rovi: Other: travel grant; Merck-Sahrp & Dohme: Other: travel grant; Daiichi-Sankyo: Other: travel grant; Takeda: Consultancy, Other: travel grant ; Jannsen: Other: travel grant; Abbvie: Consultancy, Other: travel grant; Celgene: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Other: travel and research grants; Novartis: Consultancy, Other: travel grant; Amgen: Consultancy, Other: travel grant. Diez-Campelo:Celgene BMS: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Takeda: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau; Novartis: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding, Speakers Bureau.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal